Blockchain
2 months ago
Blockchain Technology Explained Simply: How It Works and Why It Matters for the Digital Economy
What Is Blockchain Technology? A Beginner-Friendly Explanation
Blockchain technology is transforming how digital transactions are recorded, verified, and shared. Simply put, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that stores information across multiple computers instead of relying on a single central authority. This structure makes data more secure, transparent, and resistant to tampering.
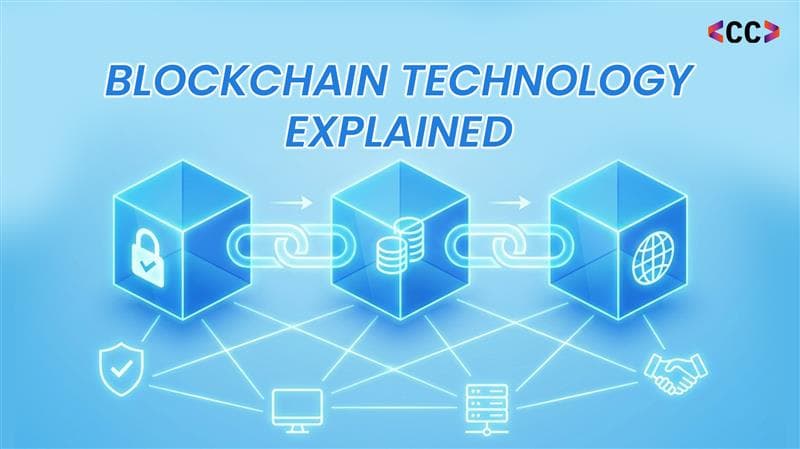
To understand how blockchain works, think of it as a chain of blocks. Each block contains a group of verified transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic link to the previous block. Once added, this data cannot be altered without changing every block that follows making blockchain one of the most trustworthy systems for digital recordkeeping today.
This concept of trust without intermediaries is why blockchain is gaining traction across industries. Businesses exploring digital transformation often turn to blockchain-based systems to improve transparency, efficiency, and accountability areas where firms like ChainCode Consulting help enterprises design real-world blockchain implementations.
The Building Blocks of Blockchain: Blocks, Chains, and Consensus
At the heart of blockchain technology are three essential components that ensure reliability and security.
Blocks store transaction data, timestamps, and cryptographic hashes that uniquely identify each block. These hashes link blocks together, forming an immutable chain.
Cryptographic hash functions play a critical role by securing data integrity. Any attempt to alter a block changes its hash, immediately alerting the network to tampering.
Consensus mechanisms determine how transactions are validated across decentralized networks. Popular methods include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Relies on computational power to validate transactions.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Uses asset ownership to confirm transactions more efficiently.
These mechanisms ensure agreement across the network without relying on a central authority—one of the reasons blockchain is increasingly adopted in enterprise-grade systems.
How Blockchain Ensures Security and Transparency
One of the biggest advantages of blockchain technology is its ability to deliver security and transparency simultaneously.
Blockchain achieves data immutability by distributing records across multiple nodes. Once data is written, it cannot be altered without network-wide consensus, making fraud and manipulation extremely difficult.
Transparency is built into the system. All participants share access to the same ledger, enabling real-time verification of transactions. Combined with advanced cryptography, blockchain protects sensitive data while still allowing authorized validation.
This balance of openness and security is why blockchain is becoming essential for industries that handle critical data—such as finance, logistics, and digital identity systems.
Real-World Use Cases: How Blockchain Is Transforming Industries
Blockchain has moved far beyond theory and is actively reshaping industries today.
In supply chain management, blockchain enables end-to-end traceability, helping businesses track products from origin to delivery while reducing fraud and inefficiencies.
In financial services, blockchain accelerates cross-border payments, reduces transaction costs, and supports decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that operate without traditional intermediaries.
Smart contracts are another powerful application. These self-executing digital agreements automatically enforce terms when predefined conditions are met—streamlining processes like insurance claims, royalty payments, and vendor settlements.
Solutions like these are often tailored for specific business needs, which is where experienced blockchain consultants, including teams at ChainCode Consulting, add value by aligning technology with operational goals.
Benefits and Challenges of Adopting Blockchain Solutions
The benefits of blockchain technology are compelling:
- Enhanced security through decentralization
- Transparent, auditable records
- Reduced reliance on intermediaries
- Improved operational efficiency
However, organizations must also consider challenges. Scalability remains a concern for high-volume networks, and regulatory uncertainty varies across regions. Successful adoption requires careful planning, platform selection, and compliance alignment.
Understanding both the advantages and limitations helps businesses implement blockchain solutions responsibly and sustainably.
Blockchain for Beginners: How to Get Started
If you’re new to blockchain, start with the fundamentals distributed ledgers, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts. Online courses, tutorials, and blockchain communities are excellent resources for beginners.
To learn faster:
- Focus on real-world use cases, not just theory
- Understand differences between public, private, and permissioned blockchains
- Stay updated on trends like Layer-2 scaling and interoperability
As blockchain continues to evolve, early understanding provides a significant advantage—whether you’re a professional, entrepreneur, or enterprise decision-maker.
Why Blockchain Is a Foundation for the Future Digital Economy
Blockchain technology is no longer optional it’s becoming foundational to how value is exchanged in the digital economy. From secure data sharing to decentralized systems of trust, blockchain is enabling new business models and operational efficiencies.
Organizations that begin exploring blockchain today position themselves for long-term resilience and innovation. With the right strategic guidance and implementation approach, blockchain can unlock opportunities that traditional systems simply cannot support.